Photo Credit: Susan Walsh/AP
Sight Gag: Place Your Bets!
Credit: Cagle
Sight Gags” is our weekly nod to the ironic, satiric, parodic, and carnivalesque performances that are an important part of a vibrant democratic public culture. These “gags” may not always be funny or represent a familiar point of view, but they attempt to cut through the lies, hypocrisy, shamelessness, stupidity, complacency, and other vices of democratic life. Of course, we invite you to comment … and to send us images that you think might deserve a laugh or at least a wry and rueful look by those who are thinking about the character of public life today.
What If They Held a Protest and No Photographers Showed Up?
Democracy relies upon dissent. Not just the theoretical possibility of protest implied by the First Amendment, but the very thing itself—flesh and blood individuals speaking truth to power and thus embodying the possibility of popular sovereignty in contexts that demonstrate both the risk and safety of political opposition. Of course, in a mass society of over 300 million people, “speaking” truth to power has less to do with words per se—although sound bytes, posters, placards, graffiti, and 140 character tweets do play a role—and more to do with visibility. Put differently, political protest is as at its root a matter of public spectacle, and its success or failure is generally a measure of who controls what is seen and by whom. Of course, governments and political operatives have known this for quite some time, and each seeks to manage the dialectic between seeing and being seen to strategic benefit. Photographers know it as well, and they too use it to strategic effects.
The NATO protests in Chicago this past weekend are an interesting case in point, as both protestors and police have jockeyed to control the public eye, each enacting what have come to be fairly conventional poses. The protestors, of course, want to be seen en masse as a way of giving a sense of solidarity and magnitude to their popular presence, but they also want to make it clear that they “see” what is going on behind the closed doors of governments and corporations. Theirs is, we might say, an attempt to embody a democratic gaze—the people seeing and being seen. Governments, on the other hand, also want to be seen, but they get caught between official political/diplomatic roles played by recognizable leaders (think of all of those photo ops you’ve seen of the heads of State shaking hands with one another, or relaxing together while watching a soccer match on the television) and the maintenance of public order, (hence lots of pictures of anonymous, paramilitary forces whose task is to “uphold the peace”). Theirs is a statist gaze or what we might call “seeing like a state.” Corporations, it seems, are generally content to remain largely invisible—their recently achieved status as individuals to the contrary notwithstanding—in a manner that implies an apolitical neutrality.
Photographers tend to capture all of this in a manner that reinforces the status quo, which is to say it underscores the sense in which our government remains democratic (dissent is allowed), even as government officials perform their tasks (leaders meet, negotiate, do their business), and the police maintain the peace (they “watch over” the scene” and “clash” with those who pose risks to public safety). Sometimes, of course, the police become over zealous and have to be reigned in (one more sign that the status quo is working) but in general they are professionals doing their job under difficult circumstances.
It is easy to be cynical of such an account, but there is a different point to be made. For such images also remind us of the importance of political spectacles as a potentially important medium of public engagement that are not entirely controlled by any one agent or set of agents, whether protestors, governments, or the media—or for that matter, the audiences that consume the images. The caption to the image above notes that the police officer shown “watches demonstrators protest” in Chicago during the first day of the NATO summit. And the point is that he wants to be seen watching—notice his stance and how he holds his baton as a visual threat to anyone who would challenge his territory or charge; indeed, the point is precisely that he needs to be seen watching in order to enact any sort of agency. But in this regard he is no different than the protestors who also need to be seen watching. Both are actors in a political spectacle.
In an important sense, democracy in particular relies on such spectacles as a way of giving presence to its effectiveness and legitimacy. And that is not an inherently bad thing, for spectacles rely upon the active involvement of a viewing audience to authenticate the experience on the ground even if its members are not directly involved in it. That said, political spectacles always come with the risk that seeing and being seen can be manipulated as absolute and hierarchical technologies of domination and control. In the photograph above, are we looking at the legitimate defender of a democratic regime or big brother? There is no final answer to that question, of course, but it is one that we need regularly and vigilantly to entertain.
Photo Credit: Joshua Lott/Getty Images North America
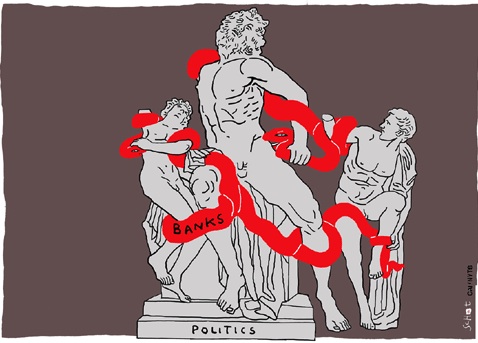
Sight Gag: The Late Modern Laocoon; or, Beauty and Economic Suffering
Credit: Bas van der Schot/De Volkskrant
Sight Gags” is our weekly nod to the ironic, satiric, parodic, and carnivalesque performances that are an important part of a vibrant democratic public culture. These “gags” may not always be funny or represent a familiar point of view, but they attempt to cut through the lies, hypocrisy, shamelessness, stupidity, complacency, and other vices of democratic life. Of course, we invite you to comment … and to send us images that you think might deserve a laugh or at least a wry and rueful look by those who are thinking about the character of public life today.
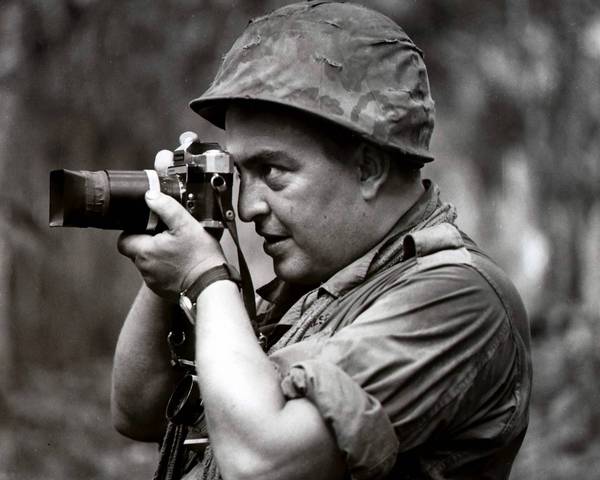
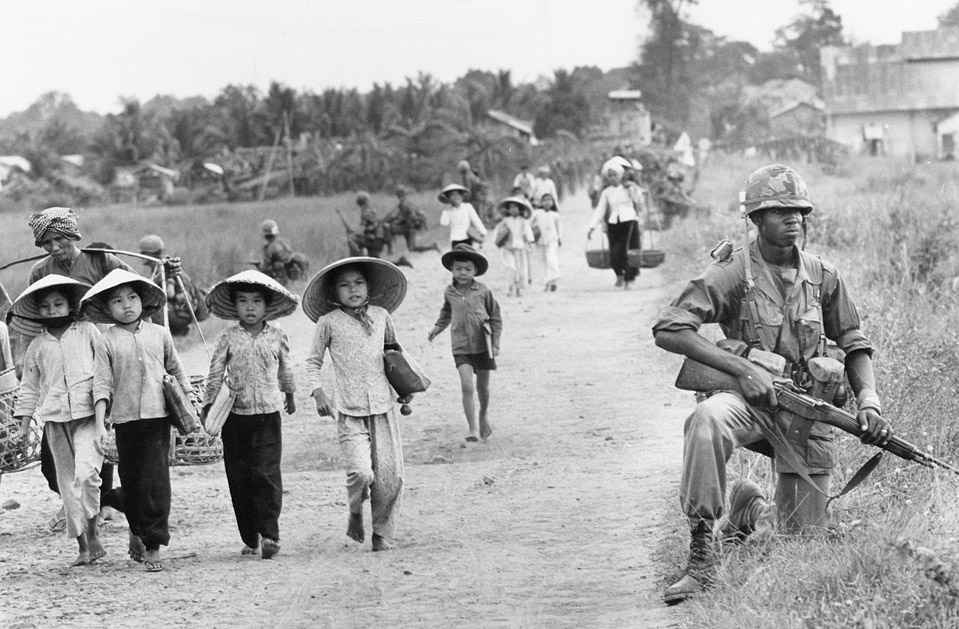
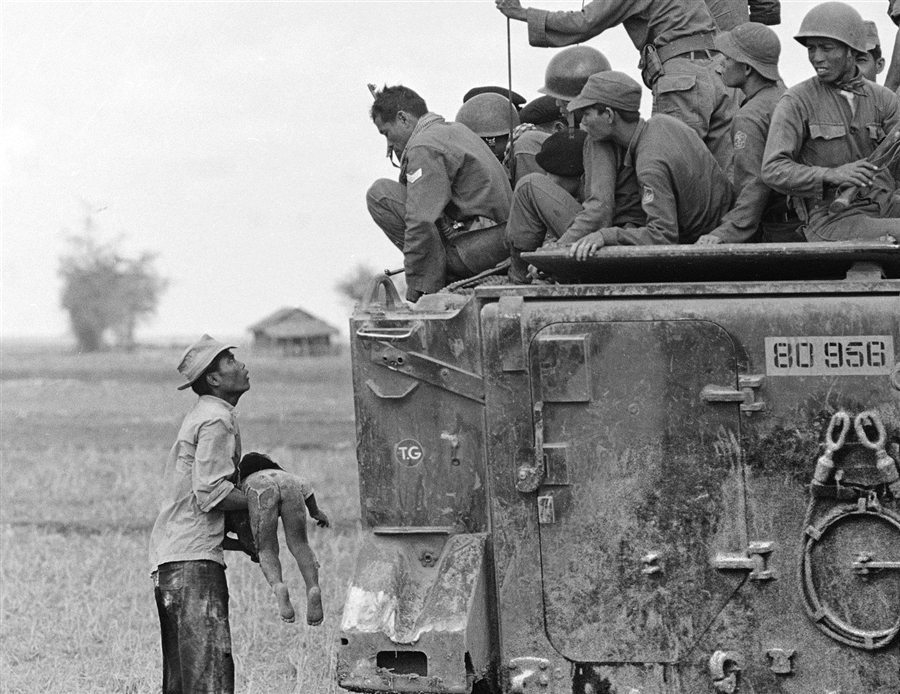
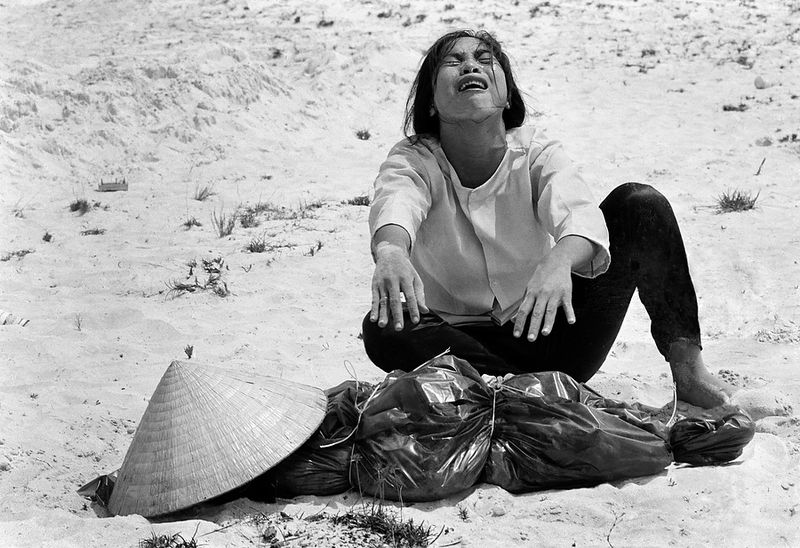
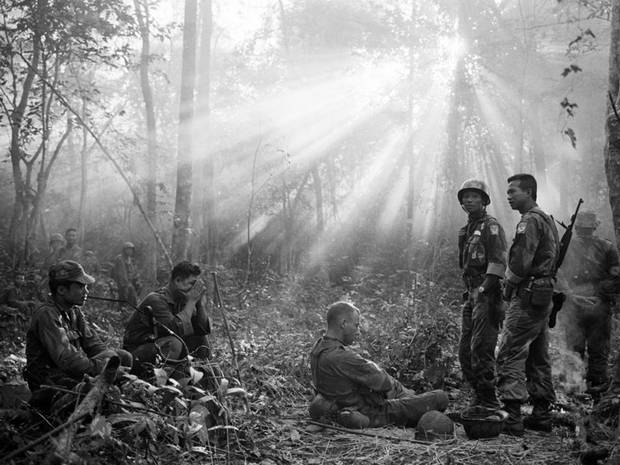
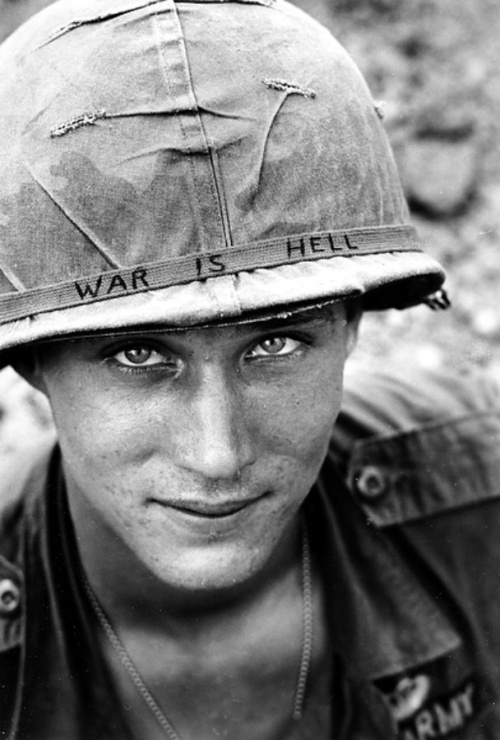
In Memoriam: Horst Faas, 1933-2012
Horst Faas photographed everything from wars in Algeria and the Congo to the 1972 Munich Olympics and much more, but he was most noted for his work in Vietnam and later the horrific conflict in Bangladesh, twice winning both the Pulitzer Prize for Photography(1965, 1972) and the vaunted Robert Capa Gold Medal (1964, 1997). By all accounts he was responsible for setting new standards for war photography. His photographs in general displayed a gritty realism and his images from Vietnam in particular depicted the execrable effects of the war on both sides of what he called “this little bloodstained country so far away.” He was chief of photo operations for the AP in Saigon from 1962 to 1972. In 1967 he was seriously wounded by a rocket propelled grenade that nearly took his life; but even then, forced out of the field and confined to a desk he was pivotal in insisting that two controversial (and ultimately iconic) photographs were distributed over the AP wire: Eddie Adam’s “Saigon Execution” and Nick Ut’s “Accidental Napalm.” He was the AP’s senior editor for Europe until his retirement in 2004.
At NCN we mourn his passing and celebrate his vital contributions to the public art of photojournalism under the most difficult of circumstances.
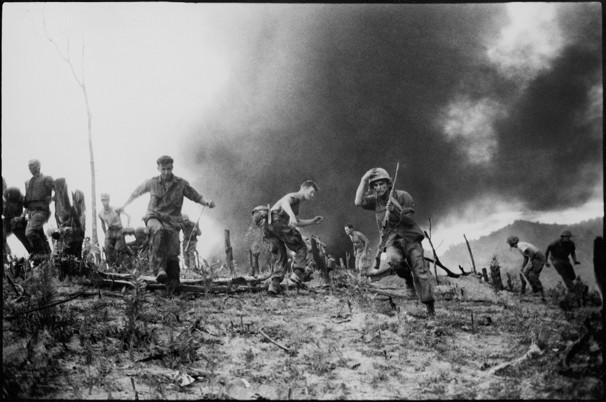

Photo Credits: Horst Faas/AP
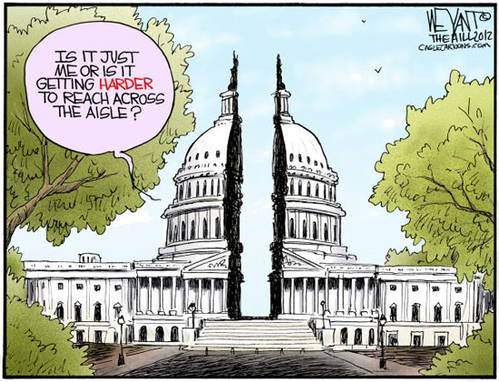
Sight Gag: The Bipartisan Politics, Reaching Across the Aisle, Searching for the Lost Center Blues
Credit: Chris Weyant/The Hill 2012
Sight Gags” is our weekly nod to the ironic, satiric, parodic, and carnivalesque performances that are an important part of a vibrant democratic public culture. These “gags” may not always be funny or represent a familiar point of view, but they attempt to cut through the lies, hypocrisy, shamelessness, stupidity, complacency, and other vices of democratic life. Of course, we invite you to comment … and to send us images that you think might deserve a laugh or at least a wry and rueful look by those who are thinking about the character of public life today.
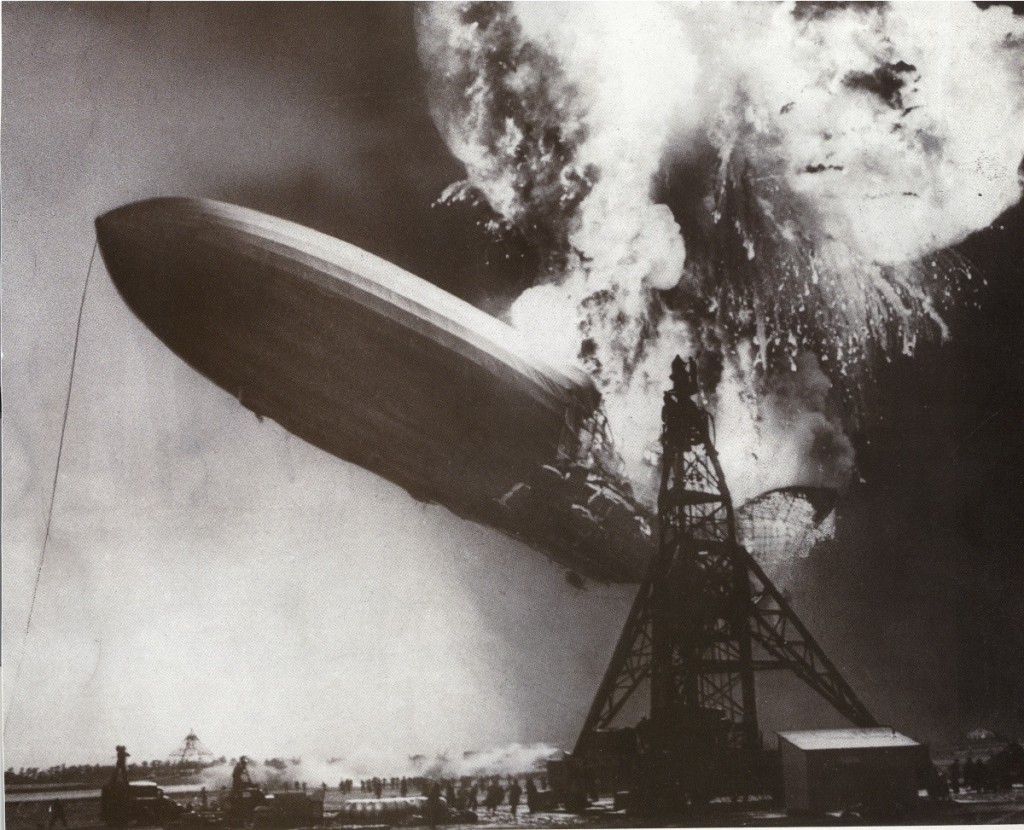
“Oh, The Humanity”: A Second Look at the Hindenburg Explosion
This past Sunday marked the 75th anniversary of the explosion of the Hindenburg in Lakehurst, NJ. As we have indicated elsewhere, when it occurred on May 6, 1936, the event, prominently depicted in the above photograph, was immediately and subsequently identified as a gothic image of a “brave new world” that invited a bleak and cautionary attitude towards the catastrophic risks of industrialization and technology—a dystopian icon of an emerging, universalized, technocratic modernity. What is especially important to note is that the explosion of the Hindenburg, resulting in 36 fatalities, was neither the first nor the most deadly of such explosions—the explosion of Britain’s R-101 dirigible killing 46 passengers five years earlier on October 5, 1930. The key difference was that in the case of the Hindenburg the media was present with live radio coverage and, of course, we have the above photograph, which quickly became the iconic representation of the disaster.
The last point is especially important, as it stands as a reminder of the centrality of the mass media in creating disasters. I don’t mean, of course, that the mass media cause disasters in a direct cause-effect fashion, but rather that what is recognized as a disaster is largely a measure of its status as a discernible “event” and outside of local and immediate experience. Such discernability is largely a function of the role that the media play in depicting and disseminating occurrences of one sort or another. As Rob Nixon has recently demonstrated in his book Slow Violence, tragedies that defy easy representation as a discrete occurrences—say disease and death caused across generations of the members of a community by toxic waste—are very difficult to cast as disasters because we simply cannot visualize their longitudinal effects. A graph marking deaths across time simply lacks the presence and verisimilitude of a photograph.
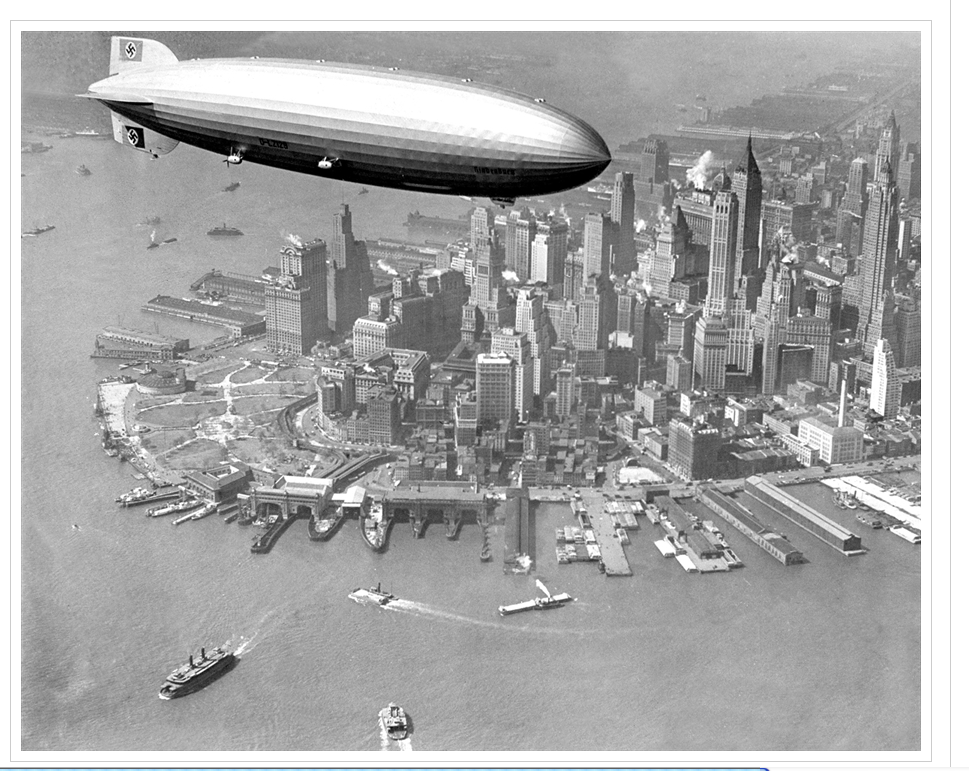
The anniversary commemoration of this event points to a different point as well. The iconic photograph above lacks any nationalistic markings of any kind. Although the name “Hindenburg” clearly designates this as a German airship, the photograph effaces that fact. It is impossible to say that this is the reason why this photograph quickly became identified as the icon for the event, but there are good reasons to believe that it didn’t hurt the cause, both because of the prevailing desire to downplay nationalist tensions between Nazi Germany and the United States, as well as the way in which such erasure made the photograph more about technology of a universalized modernity than about politics. But, of course, the extant photographic record suggests a different story. And so it is that the Atlantic frames its remembrance of the event not in terms of modernity’s gamble, but precisely in the context of international politics. So, for example, they begin with an image that shows the Hindenburg in all of its grandeur and magnitude, hovering over Manhattan. But what is most pronounced in the photograph is the swastika that sits on the tail of the vessel.
Several such images—few of which were originally seen, or at least prominently displayed in the media of the time—follow, carefully marking the national origins of the dirigible. And then, after a series of images that move the viewer through the ritualistic, everyday banality and catastrophic fatality of the attendant technological innovation of transatlantic air travel, it reinforces the nationalist origins of the whole event with photographs of a funereal scene. These photographs, replete with multiple caskets draped in swastika clad flags and Nazi salutes (images #31 and #32), are chilling in their effects, even if our contemporary reaction is marked by a presentist understanding of the horrors of Nazism that most viewers would not have been in a position to acknowledge in 1936.
The point is a simple one, but nevertheless worth emphasizing: photographs are always involved in a dialectic of showing and veiling. If we think of the iconic image in terms of how it is often captioned with reference to radio announcer Herb Morrison’s lament, “Oh, the humanity” it is easy to see how it fits within the logic of a dystopian, technological modernity. In short, it is a catastrophe that resists and challenges the positive resonance of modernity’s gamble. However, when we return the swastika to the tail of the dirigible in all of its prominence, and when we locate the event within the particular narrative of twentieth-century politics animated by Hitler’s Third Reich, the meaning of the icon is overshadowed by a much larger tragedy and its dystopian resistance to the positive affect of modernity’s gamble is mitigated if not altogether erased. It truly is a matter of what we see … or perhaps more to the point, what we are shown.
Photo Credit: Sam Shere/MPTV; AP File Photo
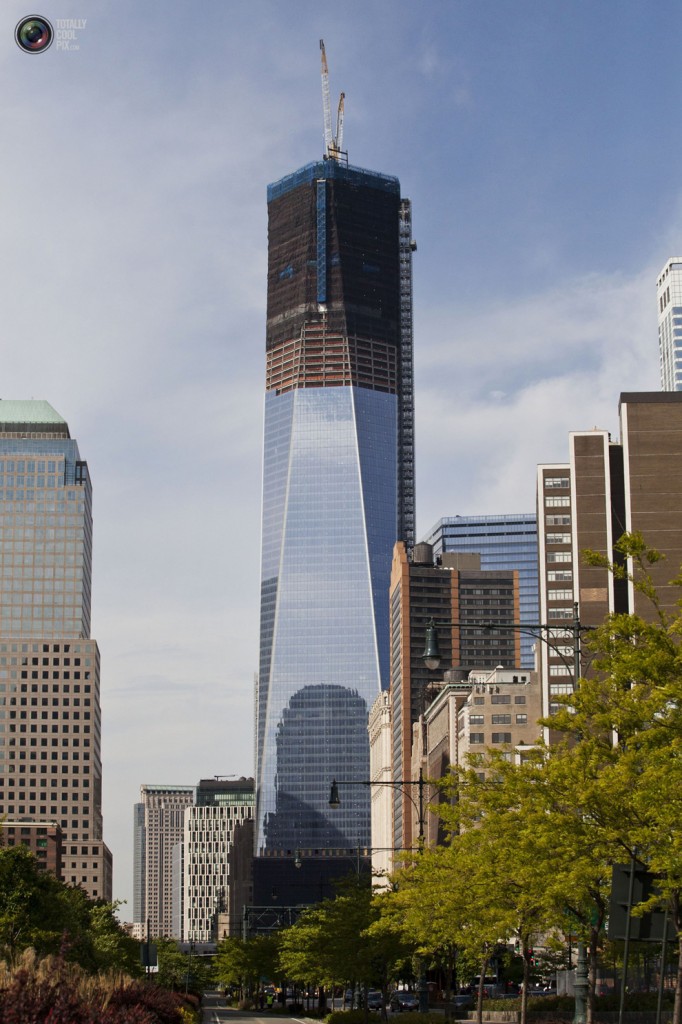
Rebuilding One World Trade Center Hollywood Style
Shot from ground level somewhere in nearby Battery Park, the photograph above features the construction of One World Trade Center (OWTC) as it nears completion slated for sometime in 2013.. This past week it grew to 1,271 feet high, making it arguably the tallest building in New York City. By the time it is completed it will sprout an additional 505 feet, to a height of 1,776 feet, and will lay claim to being the tallest building in the United States.
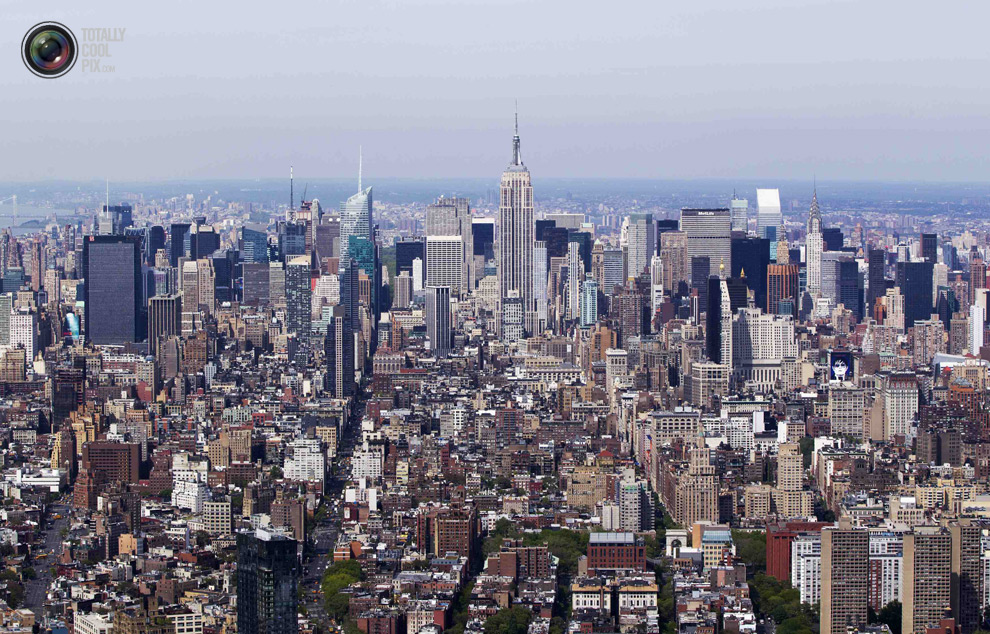
We will no doubt be seeing many pictures of OWTC in the coming year, but I was especially struck by the juxtaposition of this photograph with another in a slideshow on the building of the tower at Totally Cool Pix, shot from the 90th floor and looking out over the Empire State Building and lower Manhattan.
Although the two photographs are separated by a number of others depicting construction workers on the job, their proximity is nevertheless close enough to invoke the effect of a cinematic technique known as “shot reverse shot.” In this technique the camera reverses back and forth between two subjects so as to create the seamless appearance that they are looking at one another along a common eye line in a common space. The shot reverse shot is symptomatic of what is often characterized as the classical Hollywood style, a realist style that erases the role of the camera in the production of meaning and emphasizes a narrative structure driven by linear, chronological, and logical continuities that animates a rational, goal-oriented conclusion to a problem.
The effect here is to anthropomorphize the new tower as it both sees and is seen. In the first image the tower is an object of desire that looms over the surrounding cityscape, even as it absorbs it in its mirrored surface. It is seen from a human perspective that underscores its magnitude—sleek, polished, and standing tall— even before it achieves completion. In the second image the tower is no longer seen, but rather becomes the site for seeing. Sharing the line of sight of the new tower one looks out over Lower Manhattan, and all that one sees, including the Empire State Building, once thought of as a marvel of modern technology, is dwarfed in its presence. But more than just accenting the magnitude of scale, the view naturalizes the logical rationality of the new tower’s location within what is generally understood to be the center of U.S. business and commerce. A place for everything and everything in its place. A building was tragically destroyed, but now it remerges, Phoenix-like, from the ashes of an earlier tragedy. Nature restores itself.
The shot reverse shot logic of the relationship between the two photographs invites the viewer to locate the (re)construction of the edifice as not just another technological wonder, but as a seamless, natural event. But what exactly is the event we are being encouraged to witness? That the new building is dubbed “Freedom Tower” is not incidental in this regard, and neither is the fact that when completed it will be 1,776 feet tall—a number that recalls the origins of the new nation. In short, the relationship between the two photographs reinforces a narrative that frames an allegedly natural (re)birth of the nation in which freedom is defined as a fundamentally capitalist enterprise. That may or may not be a good story to tell, but it is perhaps equally important to note that a different photographic array—or a different visual style—might underscore the arrogance of our deification of that relationship and the implications it has for how those around the world view us.
Photo Credits: Andrew Burton/Reuters; Lucas Jackson/Reuters
SIght Gag: And So The Presidential Race Begins
Credit: Tom Toles
Sight Gags” is our weekly nod to the ironic, satiric, parodic, and carnivalesque performances that are an important part of a vibrant democratic public culture. These “gags” may not always be funny or represent a familiar point of view, but they attempt to cut through the lies, hypocrisy, shamelessness, stupidity, complacency, and other vices of democratic life. Of course, we invite you to comment … and to send us images that you think might deserve a laugh or at least a wry and rueful look by those who are thinking about the character of public life today.
The Art of Defiance
Guest Correspondent: Bryan Thomas Walsh
It is campaign season again, that phase in the cycle of American political culture when candidates from both political parties stage over-the-top displays of patriotic grandeur: they salute flags, attend baseball games, eat hotdogs at state fairs or in corner diners, shake hands with the masses, and enact an array of additional public performances that are believed to enhance one’s public image. We are, in other words, moving from the circus of the Republican primaries to the carnival of the American presidential campaign.
Given the ubiquity of hyperbolic theatrics that are so conventional to presidential campaigns, one might be taken aback by the above image. Taken just two weeks ago in Dearborn, Michigan by White House photographer, Pete Souza, the image captures President Barack Obama sitting solemnly inside of an empty, old-fashioned bus, looking intently out of the window and beyond the frame. At a glance, this is a puzzling image. Removed from the typical whirlwind of photographers, news reporters, and law enforcement, the President is seen here in a rare moment of solitude and private reflection. In many ways, the scene is neither spectacular nor conventional. It is only after reading the caption that we discover that the President is sitting in the very same bus where, almost 60 years prior, Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat to a white man, thereby igniting the Montgomery Bus Boycott and reenergizing the Civil Rights Movement.
Of course, given the superficiality that characterizes contemporary campaign spectacles, it is not hard for viewers to read this image as a mere “photo-op.” Accordingly, viewers are invited to read the reference to Rosa Parks and the Civil Rights Movement as an example of the President pandering to his liberal constituency and black voters in particular. Alternately, viewers can read this image as an attempt to frame the “first among equals” as an ordinary guy on his way to work, an image that Republican candidate Mitt Romney persistently fails to achieve. Michael Shaw at the BagNews argues that the image is an example of political “muscle-flexing,” where a crafty campaign strategy aimed at renewing the public’s opinions about the President parades around as a “candid photo involving a moment of deep reflection.”
While it is understandable for viewers to interpret this image within a cynical register, there remains something incredibly evocative and moving about the image. Indeed, the image emits an aura of authenticity – that is, it seems to capture a sincere and poignant moment where the President feels the gravity of the past and its bearing on the present or, more specifically, the role of Rosa Parks’ resistance to segregation and its relationship to the reality of Obama’s presidency. Rather than repeating the cliché and empty theatrics that saturate the campaign season, this image captures the President coming to terms with the fundamental fact that his presidency was made possible by those “second-class citizens” who defied a racist political system and executed acts of civil disobedience in hopes of realizing a more fair and equitable future for people of color. In short, the photograph serves as a history lesson insofar as it calls on viewers to recognize the role of civil rights struggles in having real effects (however oblique) on the vitality of present-day progressive politics.
But it is not only a history lesson; it is also lesson about social change. Seen here a year after the Montgomery Boycotts and the subsequent reintegration of the transportation system, Rosa Parks sits earnestly at the front of the bus alongside a visibly white passenger. The parallels between the image of Rosa Parks and the image of President Obama are striking: not only do both Parks and Obama occupy a space that was historically closed-off to blacks, but Obama unwittingly imitates the firm resolve suggested by Parks’ gaze. While the apparition of Rosa Parks reminds viewers that the Civil Rights Movement paved the way for a black man to serve as the President of the United States, she also reminds us that the vitality of contemporary democratic culture depends on the public dissent and civil disobedience of individuals and communities. One can only hope that Obama will take a hint from Rosa Parks – namely, that democratic promises are not always realized through compromises and civility; they emerge in the wake of overt and orchestrated political defiance.
Photo Credit: Pete Souza/White House; UPI/Library of Congress
Bryan Thomas Walsh is a Ph.d student of rhetoric and public culture in the Department of Communication and Culture, Indiana University. Correspondence should be sent to btwalsh@umail.iu.edu.